GeoJSON with p5js
I’m a creative coder and a GIS engineer then what I wanted to do is creative coding with GIS data.
I usually handle GIS data in GIS software off course. In this blog post, I’d like to try visualize GIS data with p5.js!
Note: This is a kind of art. The geographical precisions are out of consideration.
Prerequisites
In this post, there are some prerequisites to make the explanations easy.
- Features in the GeoJSON file are all Polygon.
- The coordinate system of the GeoJSON is geographic coordinates, which means east to west is -180 to 180 and south to north is -90 to 90.
Create the GeoJSON data
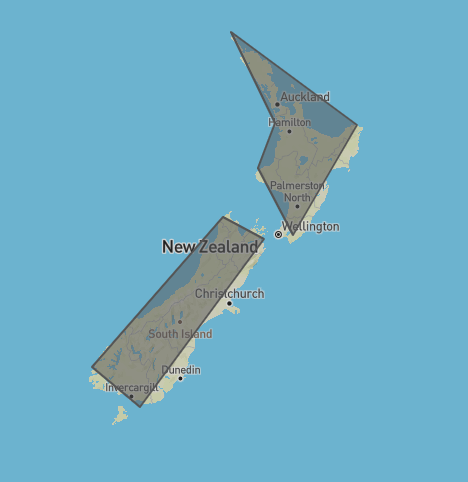
I traced NZ at geojson.io.
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[172.705078, -34.270835],
[174.638671, -37.509725],
[173.891601, -39.061849],
[175.429687, -41.310823],
[178.242187, -37.579412],
[172.705078, -34.270835]
]
]
}
},
{
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[172.353515, -40.713955],
[166.596679, -45.521743],
[168.706054, -46.739860],
[171.694335, -43.897892],
[174.155273, -41.442726],
[172.353515, -40.713955]
]
]
}
}
]
}
The GooJSON is not enough to use because of the structure requirements when you load the data in JavaScript. I need add a pair of brackets. The GeoJSON will be looks like this.
[
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": []
}
]
Save the GeoJSON as nz.geojson.
Code the sketch!
sketch.js
-
First I need to load the GeoJSON file as a object of JavaScript. Then you can call boundary in setup().
let boundary; function preload(){ boundary = loadJSON("nz.geojson"); } -
Let’s get the longitude and latitude of each polygons following the structure of GeoJSON.
-
The area of New Zealand is between 160 to 180 in longitude and -50 to -30 in latitude. To adjust these to the extent of the canvas, convert them wiht map().
-
Draw the polygons with beginShape() and endShape().
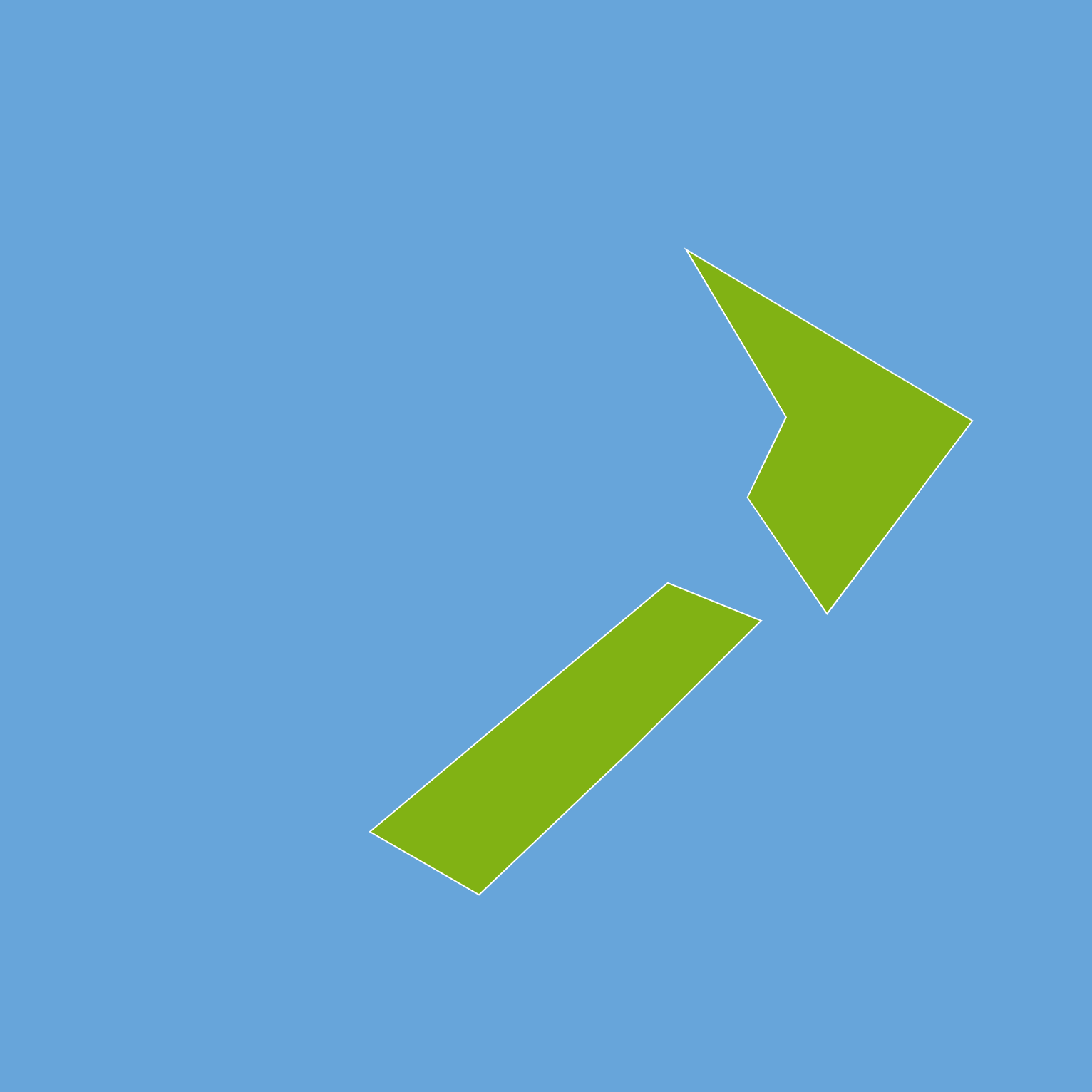
let padding = 20; function setup(){ createCanvas(windowHeight, windowHeight); background('#67a5da'); let geom; let polygons; let coords; let features = boundary[0].features; fill('#81b214'); stroke('#fff'); for (let i = 0; i < features.length; i++) { geom = features[i].geometry; polygons = geom.coordinates; coords = polygons[0]; beginShape(); for (let j = 0; j < coords.length; j++) { let lon = coords[j][0]; let lat = coords[j][1]; let x = map(lon, 160, 180, 0+padding, width-padding); let y = map(lat, -50, -30, height-padding, 0+padding); vertex(x,y); } endShape(CLOSE); } }
The final result is like this.
References
- Natural Earth: Natural Earth is a public domain map dataset.
- geojson.io: A fast, simple tool to create, change geojson.